|
Functions |
| template<typename AtomIterator1, typename AtomIterator2> |
| double | leastsquares_superposition (AtomIterator1 fixed_first, AtomIterator1 fixed_last, AtomIterator2 superimpose_first, AtomIterator2 superimpose_last, BTK::MATH::BTKMatrix &U, BTK::MATH::BTKVector &T) |
| | Calculate the transformation resulting in the least-squares superposition of two atom sets.
|
| template<typename AtomIterator1, typename AtomIterator2, typename AtomIterator3> |
| double | leastsquares_superposition (AtomIterator1 fixed_first, AtomIterator1 fixed_last, AtomIterator2 superimpose_first, AtomIterator2 superimpose_last, AtomIterator3 transform_first, AtomIterator3 transform_last) |
| | Applies the least-squares superposition of two atom sets to a third atom set.
|
| template<typename AtomIterator1, typename AtomIterator2> |
| double | get_rmsd (AtomIterator1 a1_first, AtomIterator1 a1_last, AtomIterator2 a2_first, AtomIterator2 a2_last) |
| | Calculate the superimposed RMSD of two atom sets.
|
| template<typename AtomIterator1, typename AtomIterator2> |
| double | get_trivial_rmsd (AtomIterator1 a1_first, AtomIterator1 a1_last, AtomIterator2 a2_first, AtomIterator2 a2_last) |
| | calculate the trivial (non-superimposed) RMSD between two atom sets.
|
These are iterator-based methods for optimally superimposing atomic structures, computing the RMSD between atomic structures, or both. For more information on the theory behind these methods, see this discussion of the mathematics of RMSD.
| double BTK::ALGORITHMS::get_rmsd |
( |
AtomIterator1 |
a1_first, |
|
|
AtomIterator1 |
a1_last, |
|
|
AtomIterator2 |
a2_first, |
|
|
AtomIterator2 |
a2_last | |
|
) |
| | |
Calculate the superimposed RMSD of two atom sets.
This method computes the optimal superposition of all atoms in the range [a1_first,a1_last) to all atoms in the range [a2_first,a2_last), and returns the RMSD value between the superimposed atoms. If the two sets of atoms are of unequal size, the calculation will be performed over the number of atoms in the smaller set.
| double BTK::ALGORITHMS::leastsquares_superposition |
( |
AtomIterator1 |
fixed_first, |
|
|
AtomIterator1 |
fixed_last, |
|
|
AtomIterator2 |
superimpose_first, |
|
|
AtomIterator2 |
superimpose_last, |
|
|
BTK::MATH::BTKMatrix & |
U, |
|
|
BTK::MATH::BTKVector & |
T | |
|
) |
| | |
Calculate the transformation resulting in the least-squares superposition of two atom sets.
Calculates the least-squares superposition of two sets of atoms using the method of Kabsch (Acta Cryst., 1978. A34, 827-828).
The transformation of the second atom set to the superimposed position can be recreated from the rotation matrix 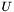 and the translation vector
and the translation vector 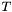 by
by 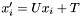
- Parameters:
-
| U | After return, contains the superposition rotation matrix. |
| T | After return, contains superposition translation vector. |
| rmsd | After return, contains the RMSD of the superimposed sets. |
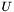 and the translation vector
and the translation vector 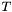 by
by 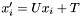
 1.5.1
1.5.1